Structural reliability assessment under creep-fatigue considering multiple uncertainty sources based on surrogate modeling approach
Author
Yuan-Ze Tang, Xian-Cheng Zhang*, Hang-Hang Gu, Kai-Shang Li, Chang-Qi Hong, Shan-Tung Tu, Yutaka S Sato, Run-Zi Wang
Periodical
International Journal of Fatigue
Abstract
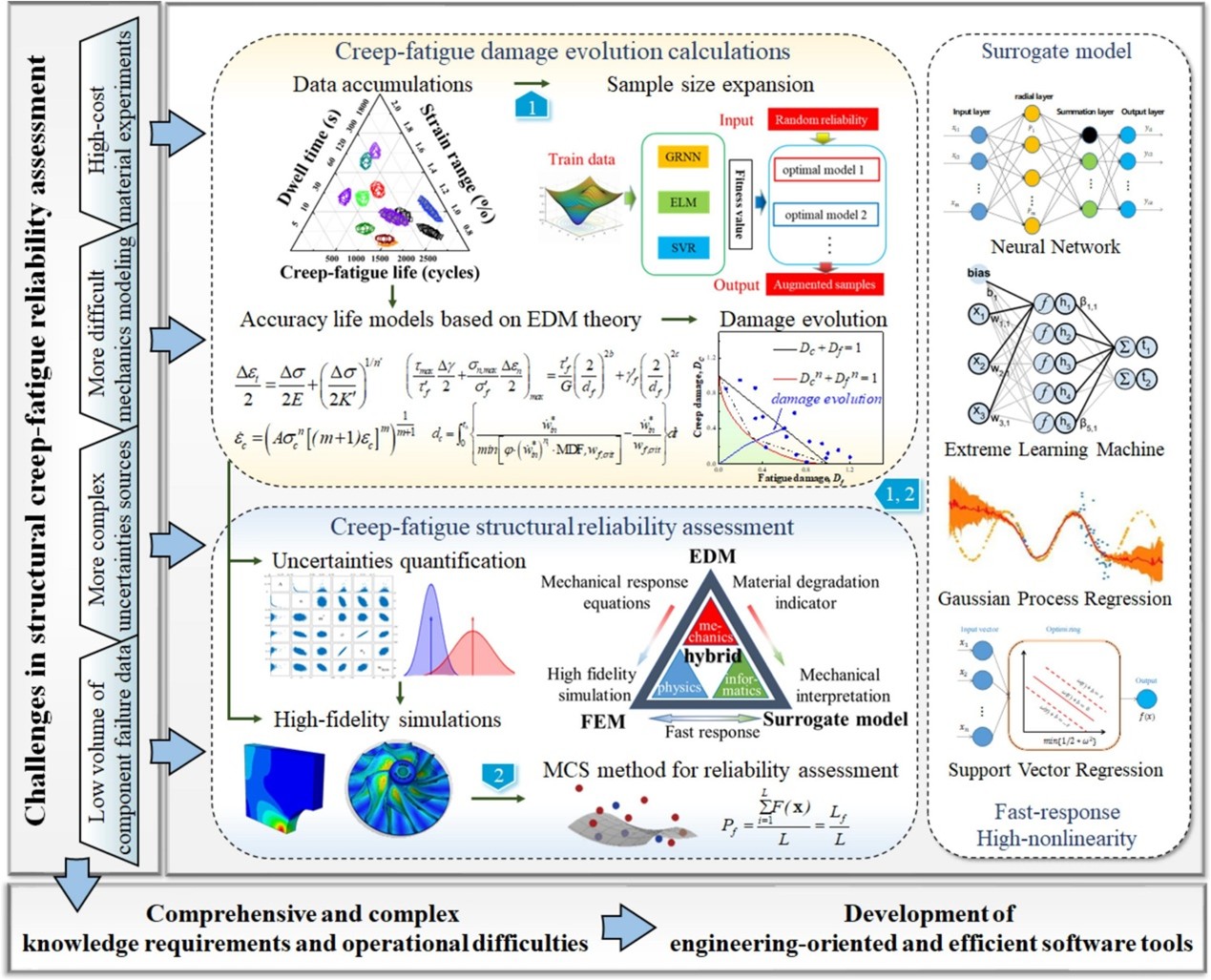
Creep-fatigue reliability assessment for high-temperature equipment is crucial but challenging due to the extensive data requirements and cumbersome methods. To enhance the implementation of creep-fatigue reliability assessment within engineering practice, this study employs multidimensional computational techniques grounded in the hybrid-driven paradigm. In detail, it presents a hybrid-driven creep-fatigue reliability assessment method integrating principles from mechanics, physics, and informatics and develops an integrated plug-in embedded in Abaqus software. The plug-in automates the implementation of parametric finite element analysis rooted in engineering damage mechanics, accommodating multiple uncertainty sources such as material properties, model parameters, geometry features, and applied loads. In particular, creep-fatigue reliability assessment utilizes a time-efficient alternative, facilitated by the adoption of surrogate modeling and Monte Carlo simulation. Furthermore, two typical examples from specimen-level (hole structure simulation specimen) to component-level (low-pressure turbine disk) are employed to demonstrate the availability and efficiency of the method and the plug-in. The plug-in with a hybrid-driven paradigm is poised to emerge as a powerful simulation-based engineering tool, facilitating the process of reliability assessment with enhanced convenience.
Keywords
Structural reliability assessment
Hybrid-driven paradigm
Creep-fatigue
Abaqus plug-in
Multiple uncertainty sources
Figure