Effects of Hertz contact rotation expansion processing on surface integrity and fatigue life improvement for a nickel-based hole structure
Author
Run-Zi Wang*, Shun Tokita, Yutaka S Sato, Le Xu, Hideo Miura
Periodical
Materials Science and Engineering: A
Abstract
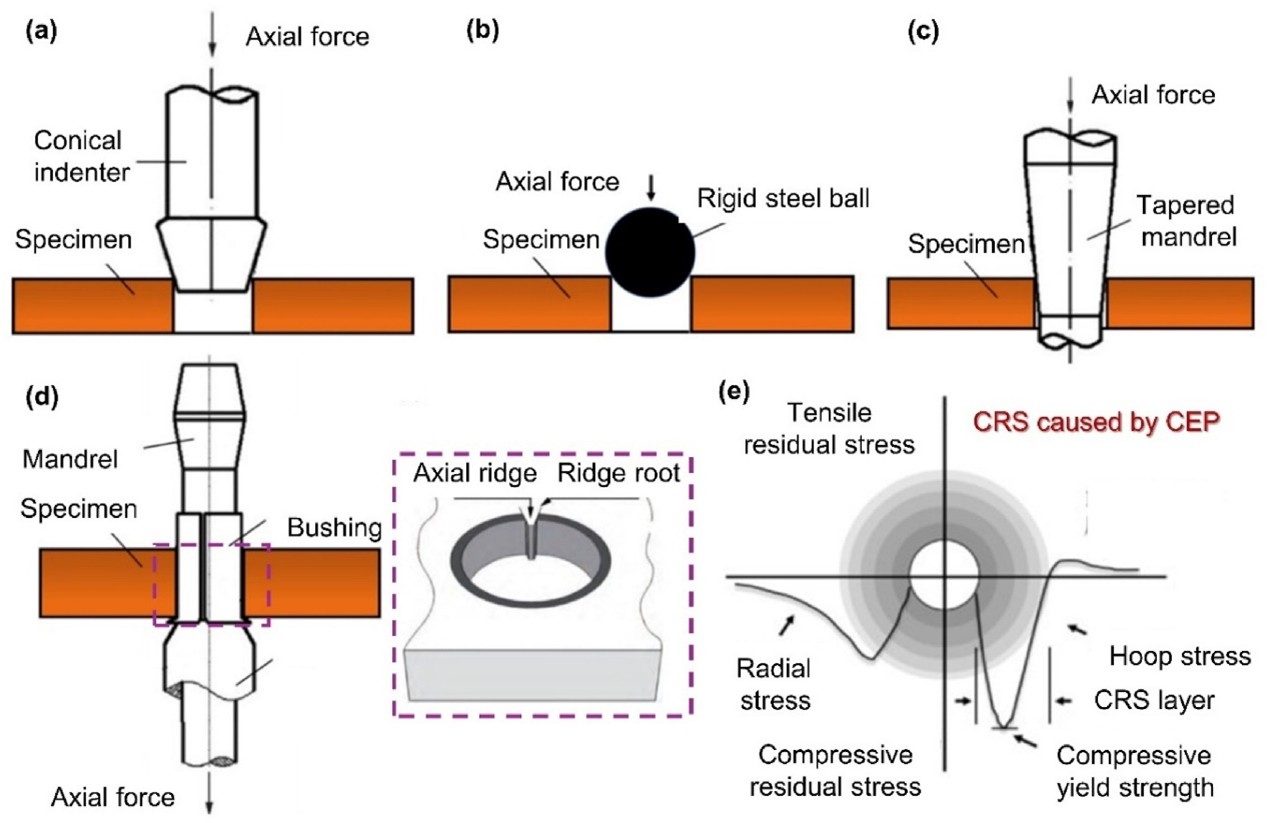
This study aims to enhance the fatigue performance of Inconel 718 superalloy components with hole structures, thereby extending their service lifetimes at elevated temperatures. In this paper, Hertz contact rotation expansion process (HCR-EP) was conducted for the strengthening of hole structures. Surface integrity distributions and evolutions were investigated and compared to that of the unstrengthening ones. Results showed that all the surface integrity factors, including surface roughness, plastic deformation layer (PDL), microhardness and compressive residual stress (CRS) layer, were significantly improved. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis of the PDL unveiled the formation of nano-grains, dislocation cells and mechanical twins, designed as the gradient microstructures. Based on the above enhancements, HCR-EP strengthening presented overall fatigue life improvements at 650 °C. The lower the stress level, the more obvious the fatigue life improvement effectiveness, as manifested by the fatigue life showing 0.32, 0.51, and 0.92 times higher than that of the unstrengthening ones. The lower the stress level, the more obvious the fatigue life improvement effectiveness. To further understand the correlation between surface integrity and fatigue life, interrupted fatigue tests combined with various characterization methods were employed, revealing excellent high-temperature stability in the fatigue-induced surface integrity evolutions via HCR-EP. The study also discussed the underlying mechanism by which slower relaxation of surface CRS leads to greater high-cycle fatigue life improvement, underscoring its potential in priority application scenarios in the future.
Keywords
Hertz contact
Hole strengthening
Surface integrity
Fatigue
Life improvement
Figure